Harnessing the Power of Yoga
A Comprehensive Guide to Strengthening Your Respiratory System

Introduction
In the hustle and bustle of our modern lives, it's easy to overlook the importance of our respiratory health. The ability to inhale deeply and effortlessly is a gift often taken for granted, but it plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. Yoga, an ancient practice that harmonizes the body, mind, and spirit, offers a wealth of tools to enhance respiratory function. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the connection between yoga and a strengthened respiratory system, delving into specific poses, breathing exercises, and the science behind these practices. Understanding the Respiratory System Before we embark on our yoga journey, let's take a moment to understand the respiratory system. Comprising the lungs, airways, and respiratory muscles, this system is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide – a process vital for sustaining life. The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle at the base of the lungs, plays a central role in breathing. When we breathe in, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, creating a vacuum that draws air into the lungs. On the breathe out, the diaphragm relaxes, and air is expelled. Yoga and Respiratory Health: A Symbiotic Relationship Yoga, an ancient practice originating in India, is much more than a series of physical postures. It encompasses a holistic approach to health, incorporating breath control, meditation, and ethical principles. Many yoga practices directly target the respiratory system, promoting lung health and overall well-being.
Breathing Techniques (Pranayama)
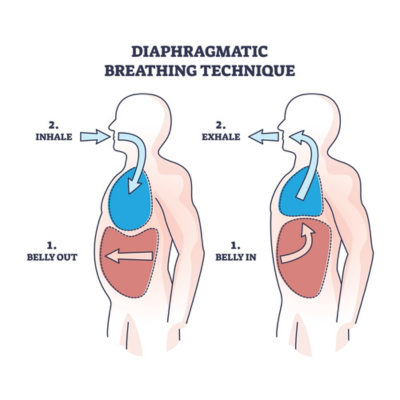
Diaphragmatic Breathing
(Dirga Pranayama):
Diaphragmatic breathing is a fundamental pranayama technique that focuses on engaging the diaphragm for deep, abdominal inhaling and exhaling. By consciously expanding the abdomen on inhalation and contracting it on exhalation, practitioners strengthen the diaphragm and improve lung capacity.
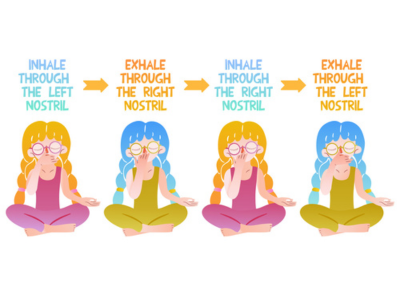
Alternate Nostril Breathing
(Nadi Shodhana):
This pranayama technique involves inhaling and exhaling through alternate nostrils, promoting balance in the nervous system and enhancing respiratory efficiency. Nadi Shodhana helps clear the nasal passages, facilitating smoother airflow.
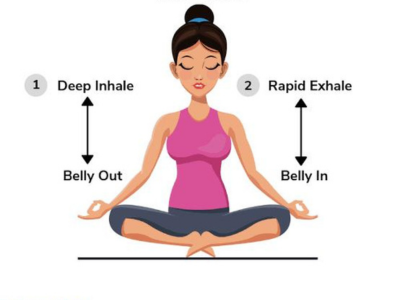
Kapalabhati Pranayama:
Kapalabhati, also known as the “skull-shining breath,” involves rapid, forceful exhalations and passive inhalations. This dynamic respiration exercise not only energizes the body but also clears the respiratory passages, fostering a sense of vitality.

Bhramari Pranayama
(Bee Breath):
The gentle humming sound produced during Bhramari Pranayama has a calming effect on the nervous system. This breathing technique promotes relaxation and can alleviate stress, which is beneficial for overall respiratory health.
Yoga Poses for Respiratory Strength
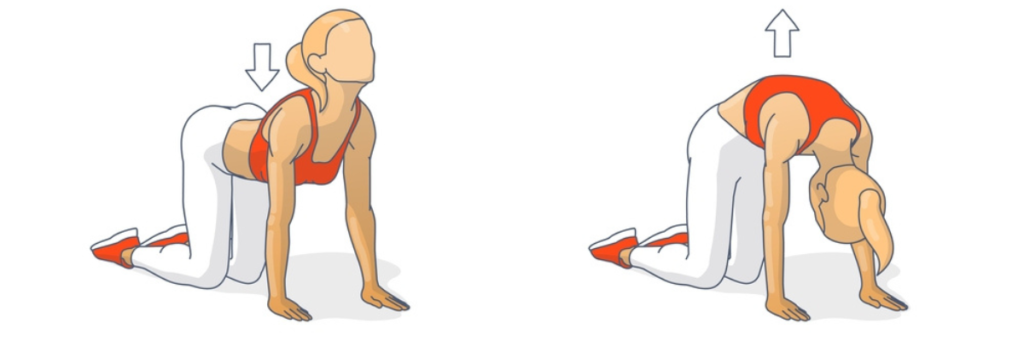
Cow-Cat Pose (Marjaryasana-Bitilasana): Flowing between the cow and cat poses helps open up the chest and improve lung capacity. The expansion and contraction of the chest in this sequence enhance the flexibility of the ribcage, facilitating deeper breathing.

Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana): Bridge pose is effective in strengthening the respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm. As the chest lifts, the lungs expand, allowing for increased oxygen intake.
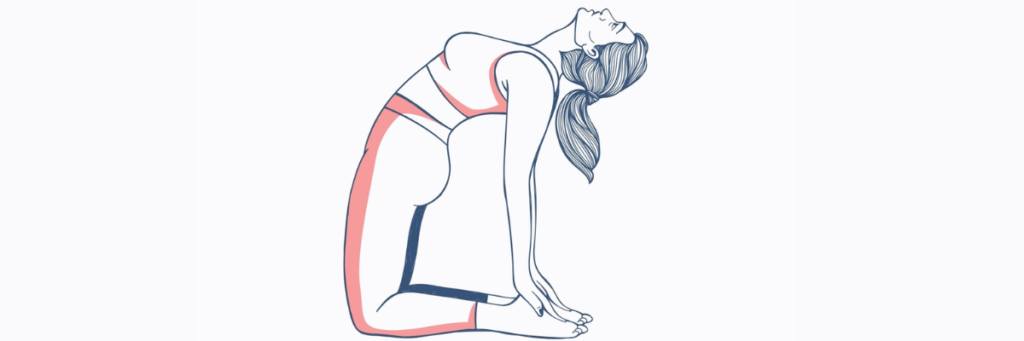
Camel Pose (Ustrasana): This backbend not only opens the chest but also stretches the lungs, promoting deep breathing. Ustrasana can be particularly beneficial for individuals looking to improve lung capacity and respiratory function.

Seated Twist (Ardha Matsyendrasana): Twisting poses like Ardha Matsyendrasana enhance the flexibility of the spine and ribcage. By incorporating these poses into your yoga practice, you encourage a full range of motion in the respiratory muscles.

Legs Up the Wall Pose (Viparita Karani): Inversions, like Viparita Karani, promote circulation and relieve stress on the respiratory system. This pose can be especially beneficial for individuals dealing with respiratory conditions.
The Science Behind Yoga and Respiratory Health
The benefits of yoga on respiratory health extend beyond the physical postures and breathing exercises. Scientific studies have explored the impact of yoga on lung function and respiratory conditions. Research suggests that regular yoga practice can lead to improvements in lung capacity, respiratory muscle strength, and overall respiratory efficiency.
Increased Lung Capacity: Yoga practices that emphasize deep, controlled inhaling and exhaling contribute to increased lung capacity. The expansion and contraction of the lungs during various poses and pranayama exercises enhance the efficiency of oxygen exchange.
Strengthening Respiratory Muscles: Yoga poses target not only the primary respiratory muscle, the diaphragm, but also secondary muscles involved in breathing. This comprehensive approach strengthens the respiratory muscles, promoting sustained and efficient breathing patterns.
Improved Respiratory Efficiency: The mind-body connection fostered by yoga contributes to improved respiratory efficiency. By cultivating mindfulness and conscious breathing, individuals become more attuned to their breath, reducing shallow inhaling and exhaling patterns that can contribute to respiratory issues.
Incorporating Yoga into Your Routine
To harness the benefits of yoga for respiratory health, consider incorporating the following practices into your routine:
Establish a Consistent Practice: Aim for a regular yoga practice, whether it’s a few minutes of pranayama and gentle stretches or a full-length yoga session. Consistency is the key to reaping the long-term benefits.
Focus on Breath Awareness: Throughout your yoga practice, prioritize breath awareness. Pay attention to the quality and depth of your breath, and aim to cultivate a steady and rhythmic breathing pattern.
Modify Poses as Needed: Observe and Listen to your body and modify poses as necessary. If you have any respiratory conditions or concerns, consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new yoga practice.
Combine Strength and Flexibility Poses: Integrate a variety of yoga poses into your practice, including those that enhance strength and flexibility. This balanced approach ensures that you address different aspects of respiratory health.
